Tina Jones Neurological Shadow Health Review Questions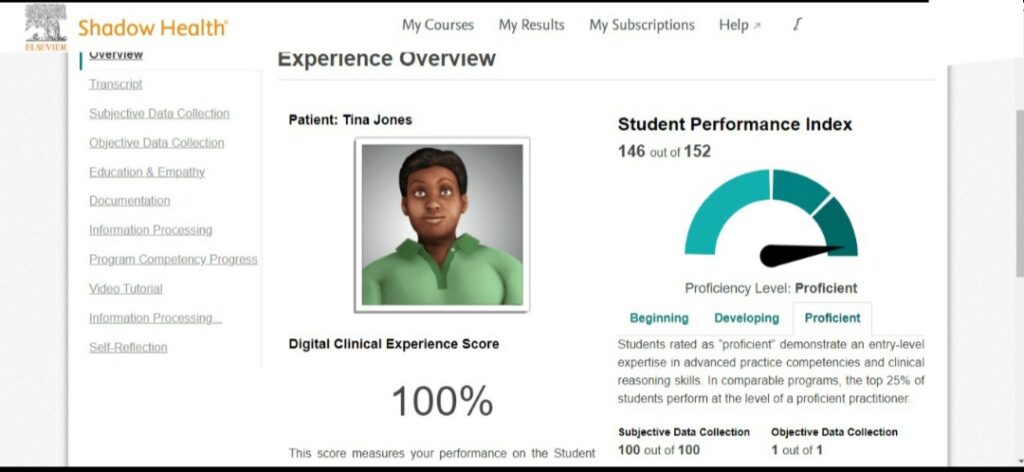
To assess spinal levels L2, L3 and L4 in Tina, which deep tendon reflexes would have to be tested?
- Achilles
- Biceps
- Patellar (Correct Response)
- Triceps
Imagine that you were preparing to irrigate a Foley catheter of a patient with a spinal cord injury at T4 in a urology clinic. Upon moving the leg bag, the patient became suddenly flushed and diaphoretic above the nipple line. What would you suspect was happening?
WE GUARANTEE A DCE SCORE OF ABOVE 95% AND HANDLE THE SOAP NOTE
- Odynophagia
- Febrile reaction
- Idiopathic spinal reaction
- Autonomic dysreflexia (Correct Response)
Which of the following is not a common symptom of Parkinson’s disease?
- Lack of facial expression
- Festination
- Cogwheel rigidity
- Intention tremors (Correct Response)
Name at least three ways to assess cerebellar function during a physical exam.
Student Response: 1. Heel-to-shin test 2. The finger-to-nose test 3. Gait and balance assessment
Model Note: The cerebellum is responsible for smooth and accurate coordination of voluntary movements. You can test cerebellar function by assessing gait and by instructing the patient to perform the finger-to-finger, finger-to-nose, heel-to-shin, rapid alternating movements, and Romberg tests.
If Tina had a fever and photophobia, you would have had to test for meningitis. Describe how you would have tested for the Kernig’s sign.
Student Response: meningeal irritation is identified using a test for Kernig’s sign and this is done by flexing the leg at the knee and hip when the patient is supine thus generating a right angle with the flexed knee, and then try to straighten the leg at the knee. If this results in pain and resistance in the lower back, it shows a positive Kernig’s sign indicating the presence of meningeal irritation.
Model Note: The test for Kernig’s sign is used to identify meningeal irritation. To perform the test, flex the leg at the knee and hip when the patient is supine, making a right angle with the flexed knee. Then attempt to straighten the leg at the knee. Resistance and pain in the lower back constitute a positive Kernig’s sign, indicating meningeal irritation.
